Fixed Radiation Source Tracking System
Overview
- Design and manufacture of location tracking monitor
- Development of central control system based on GIS
- Location change monitoring data transmission and reception and central control system DB interoperability test, reliability analysis
System Composition
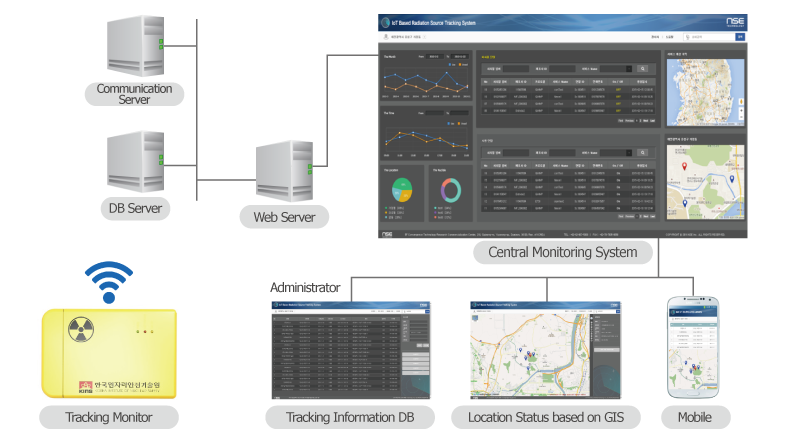
- A surveillance equipment for tracking the status of the fixed radiation source and related system facilities.
- A central control system for providing information on the monitoring status to the manager.
Features
- This system monitors the in-operation period of the fixed sources.
- RSTS (Radiation Source Tracking System) provides information on radiation source usage to the regulatory body.
- The core technology of RSTS is to detect the power source usage of the radiation source, to monitor whether the power cord is disconnected, to transmit and receive data, and to operate the central control system based on the geographic information system.
Development of Zr Recycling Process
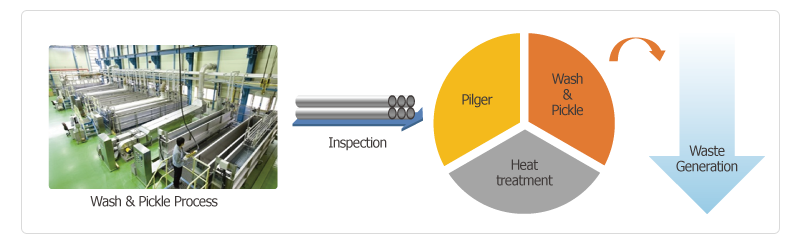
Overview
The nuclear fuel cladding tube is made through pilgering and annealing process. Pickling process is needed to remove oxide film and foreign material on the tube surface. The Zirconium(Zr) becomes dissolved in acid solution during the pickling process. Normally the pickling waste solution with the dissolved Zr is discarded as waste.
It is desirable to establish an eco-friendly full recycling plant system where the zirconium in the waste solution is fully retrieved and the waste solution is treated and re-used.
Systecm Architecture
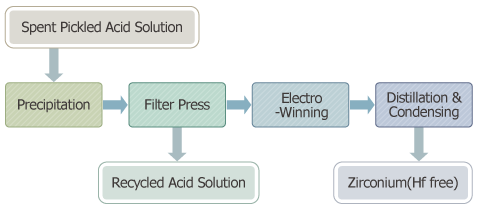
- Precipitation and Mixing
- Spent pickled acid containing dissolved Zr and precipitant(BaF2) are mix-stirred to produce precipitated salt compound containing Zr(Ba2ZrF8).
- Filter Press
- Suspending solution of spent pickled acid and precipitated salt compound are filtrated to obtain precipitated salt compound in solid phase, while the precipitate filtrate is stored in a separate tank for reuse as acid solution.
- Electro-winning
- Precipitated salt compounds are melted to produce molten salt electrolyte and electro-winning is used to deposit pure Zr on the electrodes
- Vacuum Distillation
- Zirconium condensate (ZrF4) from precipitant(BaF2) are separated and recovered by distilling and condensing the molten salt
Features
- The spent waste pickled solution generated during the process of cleaning the Zr(Zirconium) alloy cladding tube of nuclear fuel rod is re-cycled to reduce
- waste generation by more than 90%.
- Pure Zirconium and Zirconium alloys (CuZr) are deposited and re-cycled through electrowinning from the salt compound obtained by the precipitation reaction.
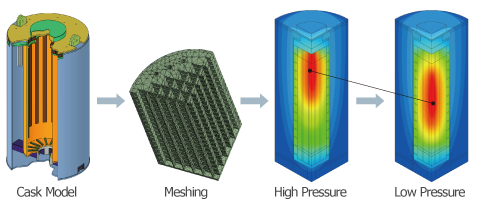
Spent Nuclear Fuel Storage Cask Monitoring
Overview
NSE Technology is developing a spent nuclear fuel(SNF) storage cask monitoring system. Since the SNF storage cask should be operated under passive natural cooling conditions without external power for over 20 years, monitoring activities are needed for thermal performance, confinement and radiation shielding requirements. This monitoring system is to detect the anomalies in confinement condition of the cask and excessive increase of fuel cladding temperature for a long period.
Composition
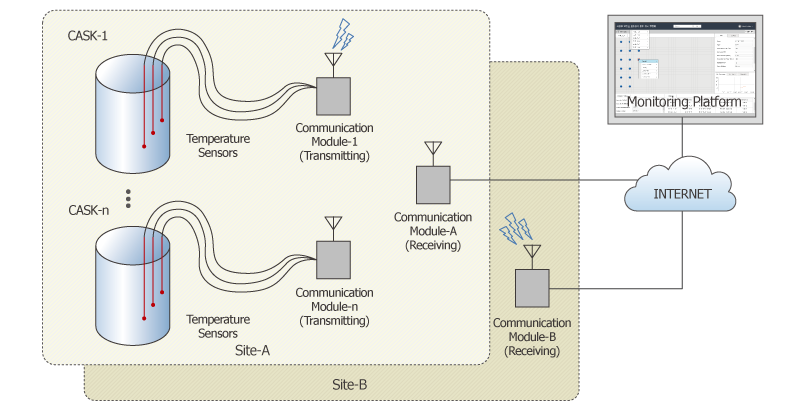
- Temperature sensors: Temperature sensors are attached on the surface of the casks.
- Transmitting communication modules: These modules are installed in each cask and they collect and wirelessly transmit signals from the temperature sensors.
- Receiving communication modules: These modules are installed at each cask placement area. These modules receive temperature signals from the transmitting communication modules and send the temperature data to the server through internet.
- Temperature and pressure algorithm sets: These algorithm sets are formulated using results from the thermo-fluid dynamic analysis on the casks and then loaded on the server.
- Integrated monitoring platform server: This server contains the database of temperature and pressure algorithm sets and decision logics for anomalies, and it provides on-screen representation of information on the cask status.
Features
- The main design goal of Cask Monitoring System is to ensure that the operating parameters of the onsite dry spent fuel nuclear fuel storage casks are maintained within the range specified in the design certificate.
- This monitoring system is designed to detect anomalies in confinement condition of the cask and excessive increase in fuel cladding temperature over a long period of time (20 years).
Core technology
- Applicable technical disciplines

- Nuclear fuel management and core design
- Nuclear fuel performance evaluation
- Computational thermo-fluid dynamics
- Core thermal-hydraulics and system analyses
- Fuel assembly critical heat flux correlations
- Reactor core protection and monitoring n
- Wired and wireless communications
- Web programming
- Major advantages
- Centralized cask condition monitoring
- Adaptability for cask types
- Flexible placement of casks
- Efficiency in management and maintenance scheduling
- Reactor core protection and monitoring n
- Lowered radiation exposure
Supply of Power Supply for NPP
Overview
The power supply used for safety and non-safety instrument and control system of nuclear power plant is recognized for its high reliability, and high quality technology.
Two switching mode power supplies (SMPS) are installed in a single bay for redundancy. Use of SMPS makes it lighter in weight and easier to maintain compared to linear type power supplies.
Type of Power Supply for NPP
- Instrument Duplication Power Supply of Plant Control System(PCS), KHNP

- Power Supply of Tritium Removal Facility(TRF), KHNP

Nuclear Safety Analysis
[Plant System Safety Analysis]
Overview
NSE Technology provides professional evaluation on the results of safety analyses performed for nuclear power plant design and licensing. Safety analysis covers LOCA analysis for evaluating the adequacy of Emergency Core Cooling System design and non-LOCA analyses. Thermal-hydraulic system codes such as MARS or RELAP5 are used, and reactor kinetics and fuel analysis codes can additionally be coupled to the system codes for detailed core evaluation during the transients.
LOCA Analysis
- Peak clad temperature
- Total amount of hydrogen generation
- Total oxidation of the cladding
- Coolability evaluation of core geometry
- Long term cooling evaluation
- Fuel rupture evaluation
- Adequacy evaluation of assumptions and uncertainties
Non-LOCA Analysis
- Loss of off-site power
- Loss of feedwater
- Boron dilution
- Feedwater pipe breaks
- Ejection of control rod assembly, etc.
- These transients are evaluated in terms of DNB, fuel melting, system pressure, dose limits, etc.
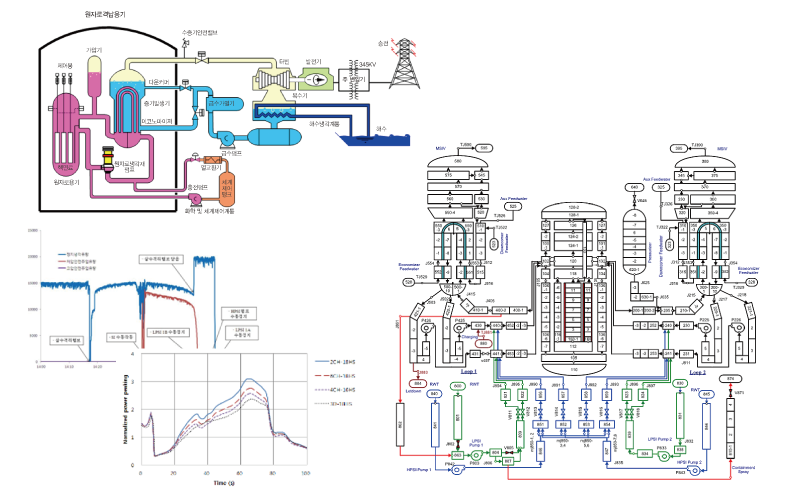
Recent Projects
- Technical support in detailed evaluation of containment spray actuation event of ShinKori Unit 1.
- RETAS workbench functional upgrade and validation on integral effect tests
- Pre-analysis on simulator for regulatory audit and training and development of a prototype engine
- Core nodalization effects in the main steam line break analysis using the MARS/PARCS Coupled Code
- Development of an Integrated Safety Analysis System Coupling Irradiated Fuel Performance Model.
[Fuel Model Coupled Safety Analysis]
Overview
- Fuel performance analysis considering fuel burnup needs to be integrated in the plant system analysis.
- Methodology has been developed for using the MARS-FRAPTRAN coupled code system
Composition
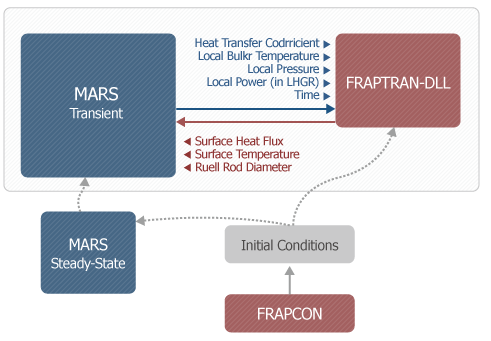
- The fuel performance modeling features of the FRAPTRAN code are integrated into the MARS code by coupling the two codes
- In the MARS/FRAPTRAN coupling calculation, the MARS code calls the FRAPTRAN-DLL which is the FRAPTRAN in DLL format
- During transient calculation, the MARS code provides the coolant parameters and rod power to FRAPTRAN-DLL calculation as boundary conditions
- The fuel depletion code FRAPCON is used for initialization calculations at given burups of fuel rods
Features
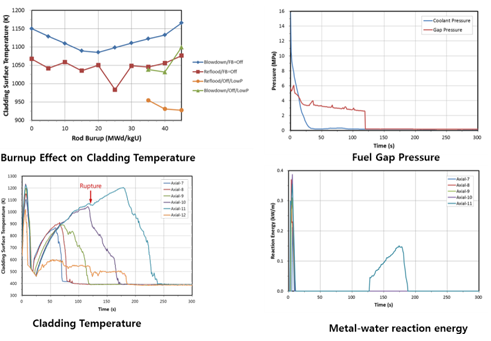
- The integrated safety analysis system is a coupled system of thermal-hydraulic systems analysis code MARS and fuel rod analysis code FRAPTRAN.
- The two codes exchange key thermal-hydraulic parameters on-line at user-specified time intervals concurrently.
- The system is capable of high fidelity safety analysis of accidents with complex thermal-hydraulic system and fuel rod interactions and behaviors in one singly executed calculation.

